Breaking! World's first living robot can now reproduce


Send us your feedback to audioarticles@vaarta.com
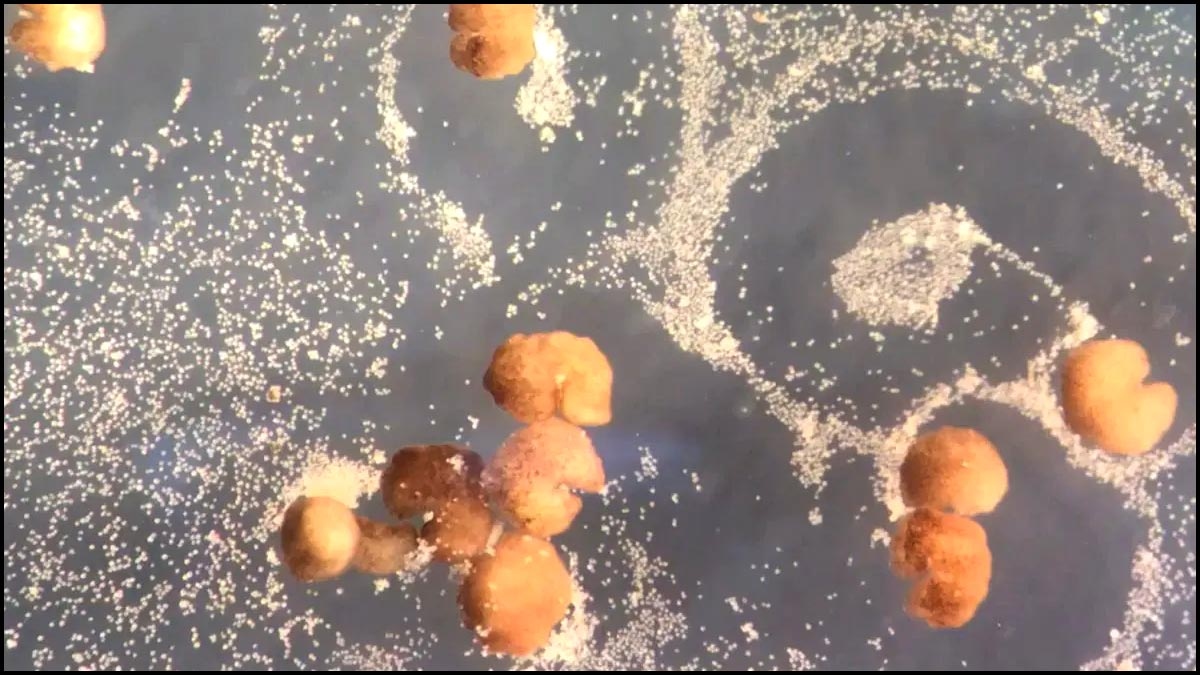



Artificial Intelligence has come a long way to explore the possibilities hidden in the world of robots. AI has enabled robots to walk, swim, and communicate. Now, they are even able to replicate themselves. New research shows that living robots can biologically replicate themselves in a unique way.
In January 2020, a team of scientists from the University of Vermont, Tufts University and Harvard University took stem cells from African clawed frog embryos and formed them into tiny living creatures called Xenobots.
The xenobots, which are less than 0.04 inches wide, were able to move on their own, communicate amongst each other and heal themselves from an injury, making them the first-ever living robots. The US scientists who created the first living robots say the life forms can now reproduce -- and in a way not seen in plants and animals.
Josh Bongard from the University of Vermont said that the xenobots made from 3,000 cells were able to replicate using "kinetic replication - a process never observed before but known to happen at the molecular level. The results of the new research were published on November 29, 2021, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Follow us on Google News and stay updated with the latest!
Comments
- logoutLogout




 Follow
Follow








-a3e.jpg)
-3c4.jpg)
-e5c.jpg)
-e66.jpg)
-71b.jpg)
-5d5.jpg)
-adc.jpg)
-798.jpg)

-7c2.jpg)




































